महाराष्ट्र अभियांत्रिकी सेवा परीक्षा अभ्यासक्रम | MPSC Engineering Services Syllabus with PDF
This Article Contains
Toggleमहाराष्ट्र अभियांत्रिकी सेवा परीक्षा अभ्यासक्रम | Maharashtra Engineering Services Exam Syllabus
महाराष्ट्र अभियांत्रिकी सेवा परीक्षा एकूण तीन टप्यात घेण्यात येते. 1. संयुक्त पूर्व परीक्षा 2. प्रत्येक संवर्गाची स्वतंत्र मुख्य परीक्षा 3. प्रत्येक संवर्गाची स्वतंत्र मुलाखत. स्थापत्य अभियांत्रिकी, यांत्रिकी अभियांत्रिकी, विद्युत अभियांत्रिकी संवर्गातील भारतीकरिता एकाच संयुक्त पूर्व परीक्षा घेण्यात येते. या सर्व परीक्षांचा अभ्यासक्रम खाली दिला आहे.
Maharashtra Engineering Services exam is conducted in three stages. 1. Combined preliminary exam 2. Mains exam for each category 3. Saperate Interview for each category. A single Combine Exam is conducted for Civil Engineering, Electrical Engineering and Mechanical Engineering. The Syllabus for every exam is given below
महाराष्ट्र अभियांत्रिकी सेवा संयुक्त पूर्व परीक्षा अभ्यासक्रम |MPSC Engineering Services Preliminary Syllabus

संयुक्त पूर्व परीक्षेत एकच प्रश्नपत्रिका असून 100 गुणांसाठी 100 प्रश्न असतात. संयुक्त पूर्व परीक्षेचा अभ्यासक्रम खाली दिला आहे.
For MPSC Engineering Services Preliminary exam there is only one Question paper which includes 100 questions for 100 marks. The syllabus for this paper is given below.
मराठी: 10 प्रश्न/10 गुण सर्व सामान्य शब्दसमूह, वाक्यरचना, व्याकरण, म्हणी व वाक्प्रचार यांचा अर्थ व उपयोग तसेच उताऱ्यावरील प्रश्नांची उत्तरे.
इंग्रजी: 10 प्रश्न/10 गुण Common Vocabulary, Sentence structure, Grammar, Use of Idioms & phrases and their meaning and comprehension of passage.
सामान्य अध्ययन: 20 प्रश्न/20 गुण १. भारताचा विशेषतः महाराष्ट्राचा इतिहास (१८५७ ते १९९०)
२. भारताचा विशेषतः महाराष्ट्राचा भूगोल
३. भारतीय अर्थव्यवस्था
भारतीय आयात-निर्यात
राष्ट्रीय विकासात सरकारी, सहकारी, ग्रामीण बँकांची भूमिका
शासकीय अर्थव्यवस्था – अर्थसंकल्प, लेखा, लेखापरीक्षण, इत्यादी
पंचवार्षिक योजना
किमती वाढण्याची कारणे व उपाय
भारतीय राज्यव्यवस्था
जागतिक तसेच भारतातील चालू घडामोडी:राजकीय, औद्योगिक, आर्थिक, सामाजिक, शैक्षणिक, भौगोलिक, खगोलशास्त्रीय, सांस्कृतिक, वैज्ञानिक इत्यादी.
पर्यावरण: मानवी विकास व पर्यावरण, पर्यावरण-पूरक विकास, नैसर्गिक साधनसंपत्तीचे संधारण विशेषतः वनसंधारण, विविध प्रकारची प्रदूषणे व पर्यावरणीय आपत्ती, पर्यावरण संवर्धनात कार्यरत असलेल्या राज्य/राष्ट्र/जागतिक पातळीवरील संघटना/संस्था.
४. अभियांत्रिकी अभियोग्यता चाचणी (Engineering Aptitude Test) (६० प्रश्न/६० गुण)I Applied Mechanics
- Matrices – Type of Matrices (Symmetric, Skew-symmetric, Hermitian, Skew Hermiitian, Unitary, Orthogal Matrices), properties of Matrices, Rank of a Matrix using Echelon forms, reduction to normal form, PAQ in normal form, system of homogeneous and non-homogeneous equations, Linear dependant and independent vectors.
- Partial Differentiation– Partial Differentiation; Partial derivatives of first and higher order. Total differentials, Differentiation of composite and implicit functions. Euler’s theorem on homogeneous functions with two and three independent variables, Deductions from Euler’s Theorem.
- Applications of Partials Differentiation, Expansion of Functions, Maxima and Minima of function of two independent variables, Jacobian, Taylor’s Theorem and Taylor’s series, Machlaurin’s series.
- Linear Differential Equations with constant Coefficients and Variable Coefficients of Higher Order-Linear Differential Equation with constant coefficients-complementary function, particular integrals of differential equation, Cauchy’s homogeneous linear differential equation and Legendre’s differential equation, Method of variation of parameters.
- Differentiation under Integral sign, Numerical Integration – Differentiation under Integral sign with constant limit of integration, Numerical Integration by (a) Trapezoidal (b) Simpson’s 1/3 (c) Simpson’s 3/8 rule.
- Double Integration- Change the order of Integration, Evolution of double integrals to compute Area, Mass, Volume, Application of triple integral to compute volume.
- Triple Integration and Application of Multiple Integrals – Application of double integrals to compute Area, Mass, Volume, Application of triple integral to compute volume.
II Engineering Mechanics
- System of Coplanar Forces – Resultant of concurrent forces, Parallel forces & Non concurrent Non parallel system of forces. Moment of force about any point, Couples, Varignon’s theorem. Distributed forces in plane, Centroid and Centre of gravity, Moment of Inertia & its theorem.
- Condition of equilibrium for concurrent forces, Parallel forces and Non concurrent Non parallel general system of forces and couples. Types of Supports, loads, beams, Analysis of trusses.
- Law of friction, Cone of friction, Equilibrium on inclined plane, Application of problems involving wedges, ladders, screw friction.
- Kinematics of particles: Velocity and acceleration in terms of rectangular coordinate system, rectilinear motion, Motion along plane curved path, Tangential and Normal components of acceleration, Motion Curves (a-t, v-t, s-t curves), Projectile motion. Relative Motion, Newton’s second law, work energy principle, D’Alembert’s principle, equation of dynamic equilibrium. Moment of Energy principles: Linear Momentum, principle of conservation of momentum, Impact of solid bodies, direct and oblique impact, impact of solid bodies, semi elastic impact and plastic impact.
III Elements of Civil Engineering
- Materials and Construction-
- Use of basic materials cement, bricks, stone, natural and artificial sand, Reinforcing Steel-Mild, Tor and High Tensile Steel.
Concrete types-PCC, RCC, Pre-stressed and Precast, Introduction to smart materials, recycling of materials.
- Substructure – Functions of foundations, (Only concepts of settlement and Bearing capacity of soils.) Types of shallow foundations, (only concept of friction and bearing pile)
- Superstructure – Types of loads: DL and LL, wind loads, earthquake considerations. Types of construction- load bearing, framed, composite. Fundamental requirements of masonary.
- Introduction to automation in construction: Concept, need, example related to different civil engineering projects.
- Use of maps and field surveys-
- Various types of maps and their uses, Principles of surveys, Modern survey method using levels, Theodolite, EDM, Lasers, total stations and GPS, Introduction to digital mapping, Measuring areas from maps using digital planimeter.
- Conducting simple and differential levelling for seeking out various benchmarks, determining the elevation of different points and preparation of contour maps, Introduction to GIS Software and other surveying soft-wares with respect to their capabilities and application areas.
- Elements of Mechanical Engineering
- Thermodynamics – Thermodynamic work, p-dV work in various process, p-V representation of various thermodynamic processes and cycles, Ideal gas equation, properties of pure substance, Statements of 1st and 2nd law of thermodynamics and their applications in mechanical engineering. Carnot Cycle for Heat engine, refrigerator and heat pump.
- Heat transfer – Statement and explanation of Fourier’s Law of heat conduction, Newton’s law of cooling, Stefan Boltzmann’s law, Conducting and insulation materials and their properties, Selection of heat sink and heat source.
- Power plants – Thermal, Hydro-electric, nuclear and solar wind hybrid power plants.
- Machine elements: Power transmission shafts, axles, keys, bush and ball bearings, Flywheel and Governors.
- Power Transmission Devices – Types of Belts and belt drives, Chain drives, type of gears, Types of couplings, friction clutch (cone and single plate), brakes (types and application only), Application of these devices.
- Mechanism: (Descriptive treatment only) Slider crank mechanism, Four bar chain mechanism, Lists of various inversions of four bar chain mechanism, Geneva mechanism, Ratchet and Paul mechanism.
- Materials use in Engineering and their Application Metals – Ferrous and Non-Ferrous, Non-metallic materials, Material selection criteria, Design Consideration, Steps in Design.
- Introduction to Manufacturing processes and their Applications – Casting, Sheet metal forming, Sheet-metal cutting, Forging Fabrication, Metal joining Processes.
- Machine Tools (Basic elements, working principle and types of operations) Lathe Machine – Centre Lathe Drilling Machine – Study of pillar drilling machine, Introduction to NC and CNC machine, grinding machine, Power saw, Milling Machine.
- Elements of Electrical Engineering
- D. C. circuit: Kirchhoff’s law, Ideal and partial voltage and current source, Mesh and nodal analysis (super node and super mesh excluded), Source transformation, Star-delta transformation, Superposition theorem, Thevein’s theorem, Norton’s theorem, Maximum power transfer theorem.
- A.C. Circuits: Generation of alternative voltage and current, RMS and average value, form factor, crest factor, AC through resistance, inductance and capacitance, R-L, R-C and R-L-C series and parallel circuits, phasor diagrams, power and power factor, series and parallel resonance, Q-factor and bandwidth.
- Three phase circuits: Three phase voltage and current generation, star and delta connections (balanced load only), relationship between phase and line currents and voltages, phasor diagrams, Basic principle of wattmeter, measurement of power by two wattmeter method.
- Single phase transformer: Construction, working principle, Emf equation, ideal and practical transformer, transformer on no load and on load, phasor diagrams, equivalent circuit, O.C. and S.C. test, Efficiency.
महाराष्ट्र अभियांत्रिकी सेवा मुख्य परीक्षा अभ्यासक्रम | Maharashtra Engineering Services Mains Exam Syllabus
मुख्य परीक्षेत प्रत्येक संवर्गासाठी वेगवेगळी परीक्षा घेण्यात येते.
महाराष्ट्र अभियांत्रिकी सेवा (यांत्रिकी) मुख्य परीक्षा अभ्यासक्रम | MES Mechanical Engineering syllabus
खाली यांत्रिकी अभियांत्रिकी मुख्य परीक्षेचा अभ्यासक्रम दिला आहे. The Syllabus for MPSC Mechanical Engineering mains exam is given below.

Paper IApplied Thermodynamics –
Zeroth law of Thermodynamics, First law of Thermodynamics, Second law of Thermodynamics, calculation of work and heat in various processes; Second law of Thermodynamics; Thermodynamics property charts and tables, availability and irreversibility, Thermodynamic relations.
Fluid Mechanics and Turbomachinery –
Fluid definition and properties, Newton’s Law of viscosity concept of continuum, Classification of fluid, Fluid statics, manometry, buoyancy, force of submerged bodies, stability of floating bbodies, viscous flow of incompressible fluid, boundary layer, elementary turbulent flow, flow through pipes, head losses in pipes. Impulse and reaction principles, velocity diagrams, Pelton-wheel, Francis and Kaplan turbines.
Heat Transfer –
Modes of heat transfer; one dimensional heat conduction, resistance concept and electric analogy, heat transfer through fins; unsteady heat conduction, lumped parameter system, thermal boundary layer, dimensionless parameters in free and forced convective heat transfer, heat exchanger performance, LMTD and NTU methods; radiative heat transfer, Stefan Boltzmann law.
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning.
Vapour and gas refrigeration and heat pump cycle; properties of moist air, psychrometric chart, basic psychrometric processes.
Internal Combustion Engine
Classification of I.C. Engine, circle Analysis of IC, SI, CI engines, Super charging/ Turbocharger Performance characteristics of SI and CI, Air pollution due to IC engine and its norms, engine fuels, engine lubricants, engine cooling, Introduction to CNG, LPG, wankle engines etc., Recent development in IC engine.
Power Plant Engineering
Thermal Power Plant- Analysis of steam cycle – Carnot, Rankine, Reheat cycle and Regenerative cycle. Layout of Power Plant, layout of pulverized coal burners, fluidized bed combustion, coal handling system, ash handling system. Forced draught and induced draught fans, boiler feed pumps, super heater regenerators, condensers, boilers, de-aerators and cooling towers.
Hydro power plant – Rainfall, run off and its measurement hydrographs, flow duration curve, reservoir storage capacity, classification of plants – run off river plant, storage river plant, pump storage plant, layout of hydroelectric power plant.
Nuclear Power Plant – Introduction of Nuclear Engineering, fission, fusion, nuclear materials, thermal fusion reactor and power plant – PWR, BWR, liquid metal fast breeder, reactors, reactor control, introduction to plasma technology. Diesel and gas turbine power plant – General layout, advantage and disadvantage component, performance of gas turbine power plant, combine heat power generation.
Renewable Energy Sources
Solar Energy – Solar concentrators and tracking, Dish and Parabolic trough concentrating generating systems, Central tower solar power plants; Solar Ponds. Basic principle of power generation in a PV cell; Band gap and efficiency of PV cells, solar cells, characteristics, manufacturing methods of mono and poly-crystalline cells; Amorphous silicon thin film cells.
Wind Energy – Basic component of WEC, Type of wind turbine – HAWT, VAWT, Performance parameters of wind turbine, Power in wind, Wind electric generators, wind characteristics and site selection; wind farms for bulk power supply to grid.
Paper IIStrength of Materials
Stress and Strain, Elastic Constants: Poission’s Ratio, Modulus of elasticity, Modulus of rigidity, Bulk modulus, Shear Force and Bending Moment diagram, Deflection of Beams, Thin Cylindrical and Spherical Shells, Strain Energy, Torsion.
Theory of Machines and Vibration
Kinematics – Structure, Machine, Link and its types, Kinematics pairs, Kinematic chain and mechanism, Grubler’s criteria, Inversions of kinematics chains, inversions of-four bar chain, single slider crank chain and double slider crank chain. Displacement, Velocity and acceleration analysis of plane mechanisms; dynamic analysis of linkages; cams; gears and gear trains; Flywheels and governors; balancing of reciprocating and rotating masses; gyroscope. Free and forced vibration of single degree of freedom systems, effect of damping, vibration isolation, resonance critical speeds of shafts.
Design of Machine Elements
Design consideration in castings & forgings, theories of failure, Design for static loadings, Design against fluctuating loads, Design of shafts, Design of springs, Design of belts.
Materials Technology
Strain Hardening, Constitution of Alloys, Iron-Carbon Equilibrium Diagram, Heat Treatment of Steels, Cast Irons, Introduction to International Standards/Codes, Non Ferrous Metals and Alloys, Fatigue Failure, Creep, Alloy Steels, Strengthening mechanism, Powder Metallurgy.
Production Process, Planning and Control
Casting, Forming and Joining Processes – Non Destructive Techniques, Mechanics of machining; basic machine tools; single and multi-point cutting tools, tool geometry and materials, tool life and wear; economics of machining; principles of non-traditional machining processes; principles of work holding, design of jigs and fixtures.
Forecasting models, aggregate production planning, scheduling, materials requirement planning.
Mechanical Measurements
Limits, Fits and tolerances; linear and angular measurements; comparators; gauge design; interferometry; form and finish measurements; alignment and testing methods; tolerances analysis in manufacturing and assembly.
महाराष्ट्र अभियांत्रिकी सेवा (स्थापत्य) मुख्य परीक्षा अभ्यासक्रम | MPSC Civil Engineering Mains Syllabus
खाली स्थापत्य अभियांत्रिकी मुख्य परीक्षेचा अभ्यासक्रम दिला आहे. The Syllabus for MPSC Civil Engineering mains exam is given below.
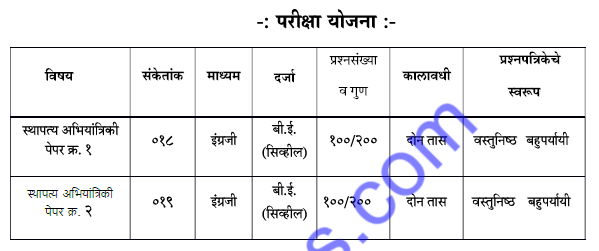
Paper I
Building Construction & Materials: Properties of wet and hardened concrete, tests on concrete, factors affecting strength of concrete, water-cement ratio, aggregate-cement ratio, mix design, additives, design of form work, types of formwork. Stones, bricks, cements, lime, mortar, timber, plastic, concrete, steel, paints and varnishes. Principles of building planning and design, integrated approach, building byelaws, building services such as vertical transportation, water supply sanitation, thermal ventilation, lighting, acoustics, fire protection, electrical fittings. Foundations, stones, brick and block masonry, steel and reinforced cement concrete structures, floors, doors and windows, roofs, finishing works, water proofing.
Strength of materials: Stresses, strains, principal stresses, bending moments, shear forces and torsion theory, bending theory of beam, deflection of beam, theories of buckling of columns.
Theory of structures: Analysis of beams, frames and trusses, slope deflection method, moment distribution method.
Structural analysis: Analysis of arches and suspension cables, influence lines, stiffness and flexibility matrix methods.
Steel structures: Design of bolted and welded connections, columns, footings, trusses, steel beams, plate girders.
Design of reinforced concrete structures (Working stress and limit state): Design of slab, beams, columns, footing. retaining walls, tanks, building frames, staircases.
Pre-stressed Concrete: Principles of pre-stressing, materials used and their properties, permissible stresses as per I.S. codes, systems of pre-stressing, losses in pre-stress, design of pre-tensioned and post-tensioned beams- simply supported, rectangular and T- beams, cable profile, end block design, bridge girder.
Construction Planning and Management: Elements of scientific management, elements of material management, safety engineering, network analysis, construction equipment, site layout, quality control.0
Computer-aided analysis and design of structures, application of computer programming to structures. numerical methods such as
i. Finding area by Simpson’s rule, trapezoidal rule;
ii. Finding root of an equation by- a) Newton-Raphson techniques
- b) Bisection method
- a) Gauss elimination method,
- b) Gauss- Jordan method,
- c) Iteration method.
महाराष्ट्र अभियांत्रिकी सेवा (विद्युत) मुख्य परीक्षा अभ्यासक्रम | Maharashtra Electrical Engineering Mains Syllabus
खाली विद्युत अभियांत्रिकी मुख्य परीक्षेचा अभ्यासक्रम दिला आहे. The Syllabus for MPSC Electrical Engineering mains exam is given below.

Paper I- Work, Power and Energy, Resistance, capacitance and inductance, DC circuits, KCL, KVL, Network theorems, fundamentals, RL, RC and RLC circuits, Steady state and transient responses. Series and parallel AC circuits, Three phase circuits, Power calculation in balanced and unbalanced circuits, Linear and non-linear loads.
- Basics of electromagnetic and electro static, series and parallel magnetic circuits, energy stored in fields, types, construction, operation of single and three phase transformers, equivalent circuit and phasor, diagrams, OC and SC tests, regulation and efficiency calculation, parallel operation, field tests before commissioning.
- Fundamentals of energy conversion, Construction and theory of DC machine, DC generator characteristics, Starting, braking and speed control of DC motors, Application of DC machines.
- Principle, types, performance characteristics, starting and speed control of single phase and three phase induction motors, Equivalent circuits, phasor diagrams, applications. VFD for induction motors. Energy saving opportunities in using VFD.
- Principle, types of synchronous motors, performance characteristics, starting and speed control of single phase and three phase synchronous motors, Equivalent circuits, phasor diagrams, applications. VFD for synchronous motors.
- Analog and Digital electronics fundamentals, devices and characteristics, amplifier and oscillator circuits, Operational amplifier, Gates, flip-flops, Combinational and sequential circuits, ADC and DACs.
- Sensors and transducers, Performance characteristics of measuring instruments, instrument transformers, measurement of physical parameters such as pressure, force, temperature, flow, vibration, torque, etc. Principles of feedback, transfer function, block diagram, steady state error, Steady state and transient specifications, Bode plot, Nyquist plot and Root locus, Relative and absolute Stability considerations.
- Power Devices- Types, Characteristics of various power electronic devices, Triggering and protection circuits, Controlled and uncontrolled rectification, DC to DC converters, DC to AC conversion, modulation techniques, SPWM. Fundamentals of electric drives, 4 quadrant operation, theory and analysis of DC drives, converter and chopper fed DC drives, Voltage, frequency and V/F controlled drives, slip power recovery schemes, fundamentals of wind power generation and grid interface.
- Power generation in India and Maharashtra, Renewable Generation, Various types of power plant, major equipment in power plants, Major issues with wind and solar power generation and grid interface. Steady state performance of overhead transmission lines and cables, per unit quantities, Bus admittance and impedance matrices, symmetrical components.
- Calculation of sag and tension in transmission of lines, Analysis symmetrical and unsymmetrical faults, principle of active and reactive power transfer and distribution. Load flow studies, steady state and transient stability, voltage stability, voltage control, economic load dispatch, load frequency control in power systems.
Paper II- Principle of circuit breaking, arc extinction and arc interruption for and DC breaker, Various types of circuit breakers and their applications, Ratings of breakers, isolators and major HV switchgear.
- Principle of over current, earth fault, differential, and distance protection. Concepts of solid state and numeric relays. Protection of generator, transformer, transmission lines, substation, busbar, induction motors. Various LT switchgear devices such as MCCB, ELCB.
- Specification of impulse wave, multistage impulse generator, insulation coordination, Routine and type tests for cables and transformers, Lightning protection, Early emission arrestors. Power quality issues, Reactive and harmonic compensation, FT devices and their applications, Passive and Active filters, HVDC transmission.
- Energy scenario in India, Energy policies, pricing and reforms, Energy conservation Act, 2001, Electricity Act, 2003. Energy management objectives, Electricity billing, electrical load management and MD control, Tariffs, PF improvements and benefits.
- Basic terms in lighting systems and features, lamp types and their features, Recommended illumination levels for various tasks, methodology of lighting system energy efficiency study, Illumination system design for residential, commercial, industrial categories. Solar powered illumination and economics associated.
- DG set selection and installation factors, Operational features, Energy performance assessment of DG sets, Energy saving majors for DG sets, Synchronization of DGs with utility supply. Parallel operation. UPS technology, types and specifications, Performance assessment.
- Pump types and characteristics, Pump curves, Factors affecting pump performance, Efficient pumping system operation, Energy conservation in pumping systems. Fan and compressor types, Fan and compressor performance evaluation and efficient system operation, Compressor capacity assessment, Energy saving opportunities in fans and compressors.
- HVAC and refrigeration system, Types of refrigeration system, Common refrigerants and properties, Compressor type and applications, Selection of suitable refrigeration system, Factors affecting performance and energy efficiency of refrigeration plants, Energy saving opportunities.
- Underground cable and cable accessories, cable in underground structure, cable installation in conduit, cable joints, cable fault detection, over-current protection and lightning protection of underground systems, operation and maintenance of underground system. Grounding systems, Equipment, Ground fault protection, Isolated neutral grounding, Grounding for hazardous locations, substation, tower grounding.
- Substation design, bus designs, substation layout, grounding and ground grid design, substation structures, major substation equipment, auxiliary equipment, substation automation, Commissioning and start up. Industrial, residential and commercial wiring, electrical system design, design and audio and video systems, Lifts and Elevator systems, safety norms and codes. Fire fighting apparatus and systems.
FAQ:
या परीक्षेचा अभ्यासक्रम पाहण्यासाठी मुख्य मेनूवरील अभ्यासक्रम (Syllabus) वर क्लिक करा. तुम्हाला MPSC च्या सर्व परीक्षांचा अभ्यासक्रम मिळेल.
ही परीक्षा एकूण तीन टप्यांत घेण्यात येते. संयुक्त पूर्व परीक्षा, प्रत्येक संवर्गाची स्वतंत्र मुख्य परीक्षा व प्रत्येक संवर्गाची स्वतंत्र मुलाखत. स्थापत्य अभियांत्रिकी, यांत्रिकी अभियांत्रिकी, विद्युत अभियांत्रिकी तसेच विद्युत व यांत्रिकी अभियांत्रिकी संवर्गातील पदांच्या भारतीकरिता एकच संयुक्त पूर्व परीक्षा घेण्यात येते.
सर्व MPSC परीक्षांच्या PDF मिळवण्यासाठी वरती एक लिंक दिली आहे. त्यावर क्लिक करून सर्व PDF मिळवा किंवा वरील मुख्य मेनू वर क्लिक करून जुन्या प्रश्नपत्रिका PDF वरती क्लिक करा.
Related Posts

राज्यसेवा परीक्षा संपूर्ण माहिती | MPSC State Service Exams

वनरक्षक भरती संपूर्ण माहिती | Forest Guard Exam All Details

